optical rotation polarimeter definition|what does a polarimeter measure : supplier Specific Rotation Equation vs. Optical Rotation – What’s the Difference? By Angelo DePalma, PHD Polarimetry using Polarimeters measure the degree of rotation of polarized light as it passes through an optically active material. Something went wrong. There's an issue and the page could not be loaded. Reload page. 163 Followers, 519 Following, 44 Posts - See Instagram photos and videos from Karina Lugo (@karinnalugo)
{plog:ftitle_list}
WPD - People die and this is the place to see it. You only have one life, don't make the mistakes seen here. . Funky Town (cartel flaying+torturing) Chechclear. Sponsored by Adidas (cartel organ extraction + cannibalism) The Guerrero Flaying (aka No Mercy in Mexico) 1 Lunatic 1 Icepick.
Specific Rotation Equation vs. Optical Rotation – What’s the Difference? By Angelo DePalma, PHD Polarimetry using Polarimeters measure the degree of rotation of polarized light as it passes through an optically active material.
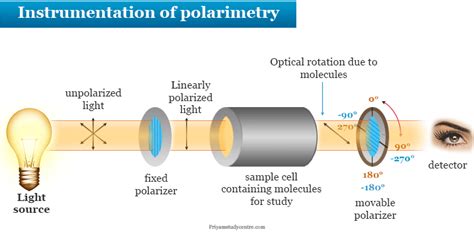
Optical rotation, also known as polarization rotation or circular birefringence, is the rotation of the orientation of the plane of polarization about the optical axis of linearly polarized light as it travels through certain materials. Circular birefringence and circular dichroism are the manifestations of optical activity. Optical activity occurs only in chiral materials, those lacking microscopic mirror . Polarimeter is the instrument that measures the direction and angles of rotation of plane-polarized light. The plane-polarized light pass through the sample tube containing the solution of sample, and the angle of .A polarimeter is an optical instrument with which one can accurately measure the angle by which the polarization of light is rotated e.g. when it passes through an optically active medium (containing chiral molecules).Recording optical rotation with a polarimeter: The plane of polarisation of plane polarised light (4) rotates (6) as it passes through an optically active sample (5).This angle is determined with a rotatable polarizing filter (7).. In chemistry, specific rotation ([α]) is a property of a chiral chemical compound. [1]: 244 It is defined as the change in orientation of monochromatic plane .
Optical activity is measured by a polarimeter, and is dependent on several factors: concentration of the sample, temperature, length of the sample tube or cell, and wavelength of the light passing through the sample. Rotation .Definition of polarimetry. Polarimetry is a superior, sensitive and nondestructive measuring technique for the measurement of optical activity, as exhibited by inorganic as well as organic compounds. . The measured value in a .
Specific Rotation— The reference Specific rotation 781S in a monograph signifies that specific rotation is to be calculated from observed optical rotations in the Test solution obtained as directed therein. Unless otherwise directed, measurements of optical rotation are made at 589 nm at 25.Where a photoelectric polarimeter is used, a single measurement, corrected for the .The optical rotation is measured through a polarimeter. The optical activity of optically active substances is studied by the polarimeter. Polarimetry Gives the measurement of rotation of plane-polarized light by an optically active substance. . The Optical Rotation Definition. The phenomenon of optical rotation was studied in detail by Biot .
A polarimeter is the basic scientific instrument used to make these measurements, . (also known as optical rotation or optical rotary dispersion), linear dichroism, circular dichroism and scattering. [8] To measure these various properties, there have been many designs of polarimeters, some archaic and some in current use.
Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\): The effect of path length on optical rotation. The longer the path of light through a solution of molecules, the more molecules will be encountered by the light, and the greater the optical rotation. The value of the optical rotation must be corrected for the length of the cell used to hold the sample.Optical rotation is measured with an instrument called a polarimeter. It produces plane-polarized light and passes it through a sample of liquid and measures the angle through which the plane of vibration of the plane-polarized light is rotated as it passes through a sample. . Optical rotation measurements are most commonly used to confirm .The optical rotation is the angle through which the plane of polarization is rotated when polarized light passes through a layer of a liquid. Substances are described as dextrorotatory or levorotatory according to whether the plane of polarization is rotated . Optical rotation is measured with a polarimeter. The zero point of the polarimeter .
The plane of polarization can be determined by an instrument called a polarimeter, shown in the diagram below. Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\): Operating principle of an optical polarimeter. 1. Light source 2. Unpolarized light 3. Linear polarizer 4. Linearly polarized light 5. Sample tube containing molecules under study 6. Optical rotation due to .Determine the optical rotation of this filtrate in a 200-mm polarimeter tube. To approximately 35 mL of the filtrate in a 50-mL flask, add 1.5 g uranyl acetate dihydrate, and keep in the dark for 30 minutes with occasional swirling. Filter and determine the optical rotation of the clear solution of uranyl malate complex.Schematic of a polarimeter. When an optically active substance is present in the beam, it rotates the polarization of the light reaching the analyzer so that there is a component that reaches the detector. The angle that the analyzer must be rotated to return to the minimum detector signal is the optical rotation, .The value of the optical rotation must be corrected for the length of the cell used to hold the sample. In summary: \[[\alpha] = \frac{\alpha}{c \times l} \nonumber\] a is the measured optical rotation. c is the sample concentration in grams per deciliter (1 dL = 10 mL). That is, c = m / V (m = mass in g, V = volume in dL). l is the cell length .
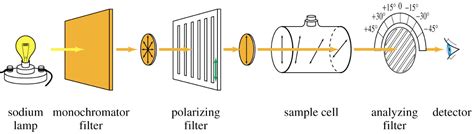
This notation means that the measurement was conducted at 25 o C using the D-line of the sodium lamp (λ=589.3 nm). A sample containing 1.00 g/mL of the compound in a 1 dm tube exhibits an optical rotation of 3.5 o in clockwise direction. Note that the instrument used in Chem 30BL and Chem 30CL can provide the specific optical rotation, which already corrects the .Optical activity is the ability of a substance to cause optical rotation or circular dichroism: Optical rotation is the phenomenon that the polarization direction of light is gradually rotated clockwise (dextrorotary) or anti-clockwise (levorotary) .Definition of polarimetry. Polarimetry is a superior, sensitive and nondestructive measuring technique for the measurement of optical activity, as exhibited by inorganic as well as organic compounds. . The measured value in a .Polarimeters are essential instruments for analyzing the optical properties of substances. These devices measure the rotation of polarized light as it passes through a sample, providing valuable information about the chemical .
Polarimetry, in analytic chemistry, measurement of the angle of rotation of the plane of polarized light (that is, a beam of light in which the vibrations of the electromagnetic waves are confined to one plane) that results upon its passage through certain transparent materials. Polarimetry is ofThe meaning of POLARIMETER is an instrument for determining the amount of polarization of light or the proportion of polarized light in a partially polarized ray.
The polarimeter is an instrument that measures the direction and angles of rotation of plane-polarized light. The plane-polarized light passes through the sample tube containing the solution of a sample, and the angle of rotations will be received and recorded by the analyzer, as summarized in Fig. 5.4c.. Figure 5.4c Measurement of Optical Rotation with Polarimeter 8. Types of Optical Isomers • Isomer that rotate light in a clockwise direction as viewed toward the light source are “dextrorotatory”, or “(+) optical isomers”, and those that rotate light in a counterclockwise direction are called “levorotatory” or “(-) optical isomers”. • Note:The symbols d- and l-, formerly used to indicate dextrorotatory and levorotatory isomers, but l .The rotation degree measured by the polarimeter is called the observed rotation (α), and the observed rotation depends on the length of the sample tube, concentration of the sample and temperature. To compare the optical rotation between different compounds under consistent conditions, the specific rotation is used.FOOD AND NUTRITIONAL ANALYSIS | Fruits and Fruit Products* R.J. Pither, in Encyclopedia of Analytical Science (Second Edition), 2005 Polarimetry. The determination of sucrose and reducing sugars in fruit and fruit products by polarimetry is an AOAC recommended method. The polarimeter measures the rotation of plane polarized light caused by a solution containing an .
An easily constructed and inexpensive polarimeter with an optical rotation angle resolution of about 0.5° is presented. It is made from small pieces of polarizing film, 2 LEDs, a protractor, and a few wires, all held in place with plastic interlocking toy bricks, such as Lego bricks. The instrument was used to demonstrate the optical rotation of plane polarized light .
why polarimeter is used
Laurent’s Half-Shade Polarimeter is an optical instrument used to measure the optical rotation of substances, typically liquid solutions containing optically active compounds. These compounds have the ability to rotate the plane of polarization of linearly polarized light, a property that can be exploited to determine the concentration, purity, or specific rotation of the .A useful model for explanation of optical rotation considers that a beam of plane-polarized light is the vector resultant of two oppositely rotating beams of circularly polarized light. This will be clearer if we understand that circularly polarized light has a component electric field that varies in direction but not in magnitude so that the .
The AUTOPOL II Automatic Polarimeter is a general-purpose polarimeter with ±0.01 Degrees Optical Rotation accuracy. This accuracy is applicable for food, university education, many chemical, flavor and fragrance applications, as well as .
bearing seal test
7 de jan. de 2011 · BLOG DO COSME RÍMOLI – Ser um apreciador do mundo esportivo não é fácil. Existem tantas notícias que acontecem no mundo dos esportes, que fica difícil acompanhar tudo de uma só vez. No mundo do futebol, também não é diferente.Por isso que existem profissionais como Cosme Rímoli, que escrevem artigos diários sobre as .
optical rotation polarimeter definition|what does a polarimeter measure